Convolutional neural network (CNN) applied to respiratory motion detection in fluoroscopic frames
International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery 2019
Abstract
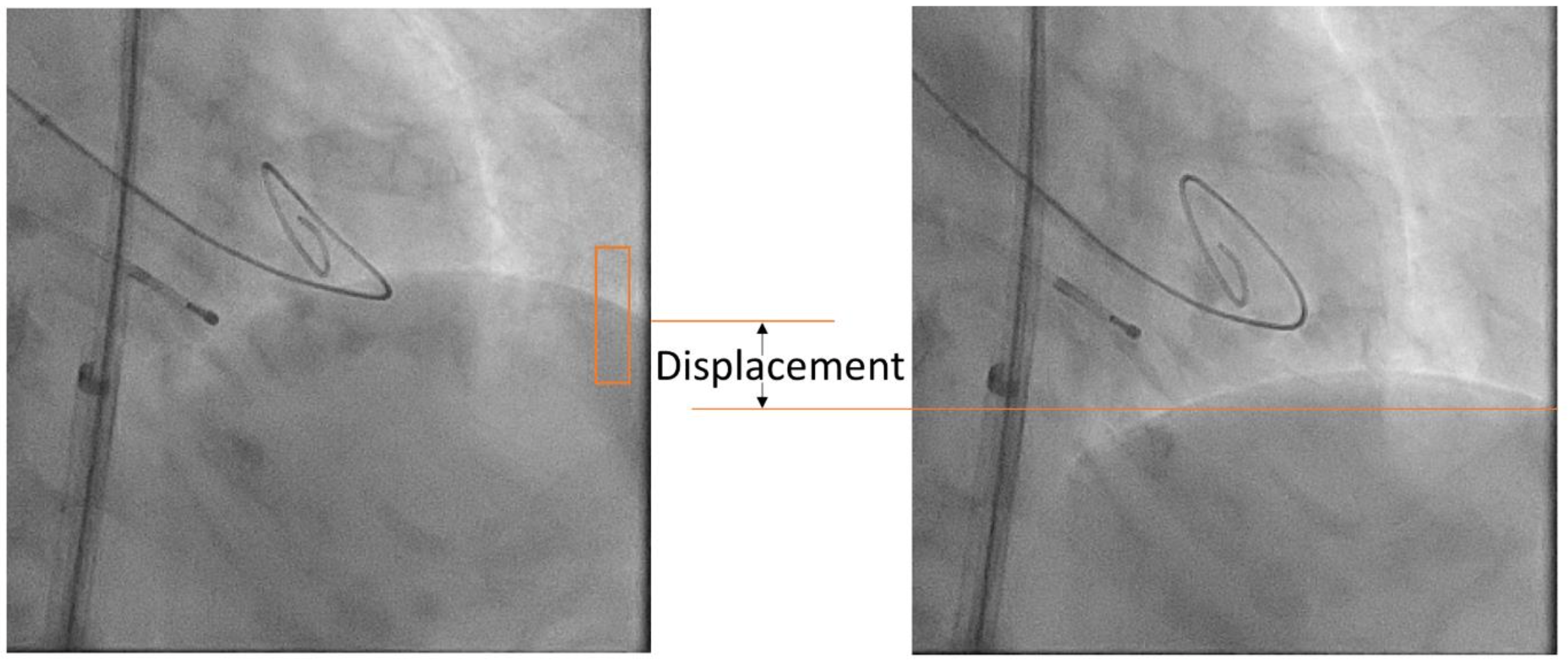
X-ray (XR) fluoroscopy provides real-time images and allows physicians to see the internal structure and function of a patient thus yielding an essential technique for guiding cardiovascular interventions. The weaknesses of XR in imaging soft tissues can be addressed by augmenting real-time fluoroscopy with organ shape models derived from e.g. preinterventionally acquired CT angiography (CTA). Following initial registration, respiratory motion is a major cause of introducing mismatch to the superposition. If this motion can be extracted from the fluoroscopy, the model overlay position can be adjusted accordingly, and the mismatch can be reduced. Convolutional neural networks (CNN) have been shown to be a powerful technique in image related tasks. This project aims to evaluate CNNs as a novel approach to extract respiratory motion from fluoroscopic runs.
Bibtex
@article{baldauf2020convolutional,
title={Convolutional neural network (CNN) applied to respiratory motion detection in fluoroscopic frames},
author={Baldauf, Christoph and B{\"a}uerle, Alex and Ropinski, Timo and Rasche, Volker and Vernikouskaya, Ina},
year={2019},
journal={International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery},
volume={14},
pages={14--15},
issue={14},
doi={10.1007/s11548-019-01969-3}
}